BEVITOR伟德
2023年优秀大学生数学国际夏令营
日程安排

中国·开封
2023年7月4—8日
BEVITOR伟德
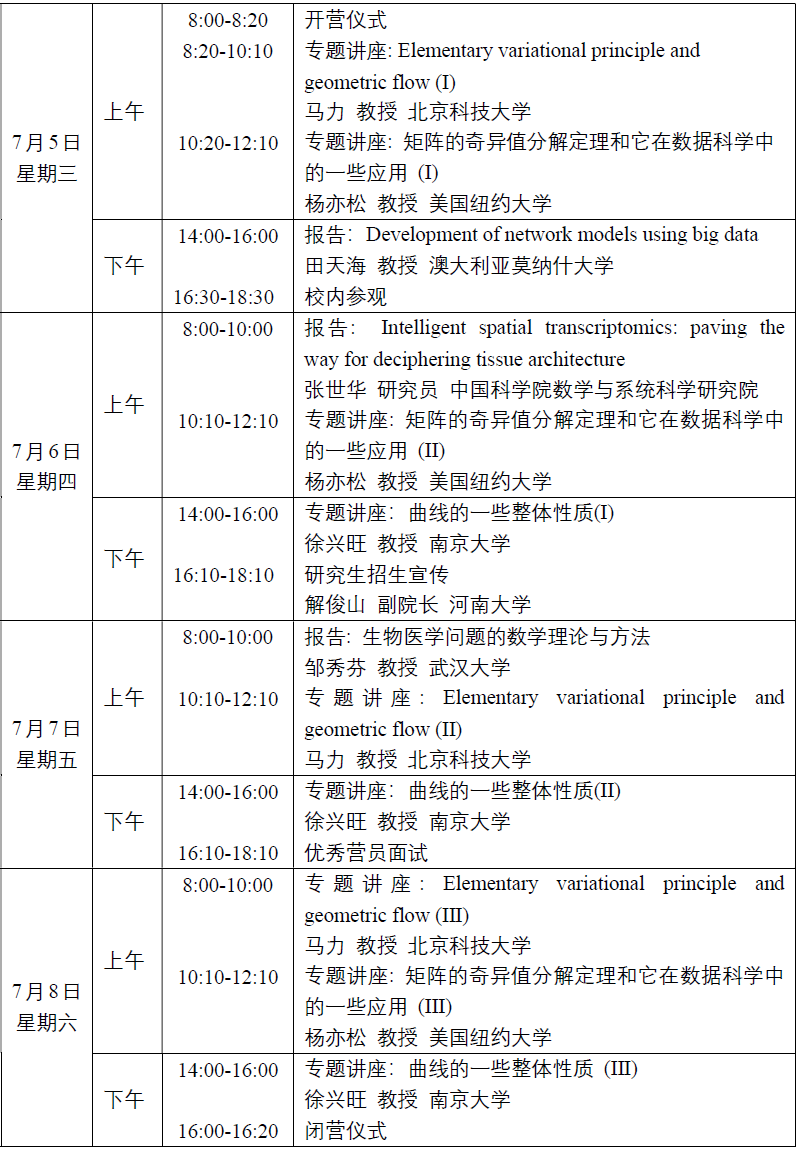
2023年优秀大学生数学国际夏令营日程安排
为促进高校之间优秀大学生的交流和互动、给学生提供一个了解数学和统计学科各个方向最新前沿动态的机会,BEVITOR伟德拟定于2023年7月4日—7月8日举办大学生数学夏令营。本次夏令营计划在全国高校范围内招收40名数学、统计学及相关专业的高年级本科生,来我院进行集中交流。
我们邀请到以下国内外专家为学生讲授专题讲座、作前沿报告:
杨亦松 教授 美国纽约大学
马 力 教授 北京科技大学
徐兴旺 教授 南京大学
张世华 研究员 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院
邹秀芬 教授 武汉大学
田天海 教授 澳大利亚莫纳什大学
BEVITOR伟德
2023年优秀大学生数学国际夏令营日程安排
讲座题目与摘要
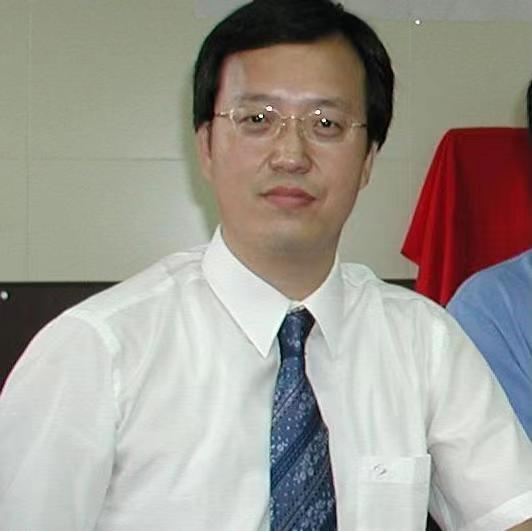

报告人: 马力 教授 北京科技大学
题 目: Elementary variational principle and geometric flow
摘 要: In this lecture series, we introduce the elementary variational principle and geometric analysis. In the first lecture, we present some basic material such that the divergence theorem, Liouville theorem for harmonic functions, minimizing harmonic mappings, minimal surfaces, the fundamental lemma of calculus of variation, the Dirichlet principle, eigenvalues and eigenfunctions in the Sturm-Liouville theory. In lecture two, we present the maximum principle, solvability of some linear elliptic and parabolic problems, and the application of elliptic equation to the proof of isoperimetric inequality. In lecture three, we consider the one-dimensional minimal surface flow, which is about the length shortening of evolved curves. We derive various integral estimates, show the global existence of the solution, and study its asymptotic behavior at time infinity. Further research topics can be found the literature listed.

报告人: 杨亦松 教授 美国纽约大学
题 目: 矩阵的奇异值分解定理和它在数据科学中的一些应用
摘 要: 矩阵或者映射的奇异值分解定理(SVD),是线性代数里面一个对现代应用数学,特别是机器学习和数据科学(包括统计学),一个非常重要和有效的、富于理论深度和计算构造性的结果。在这个短课程里,我们将介绍SVD和它在数据科学中的几个重要应用,包括数据的低维最优逼近问题和主分量分析问题。

报告人: 田天海 教授 澳大利亚莫纳什大学
题 目: Development of network models using big data
摘 要: Network model is a powerful tool to explore complex relationship between variables in big datasets. Different research areas have different motivations to develop network models. In finance and economics, researchers are interested in the structure of networks in terms of cluster and community. In biology, the key question is whether a molecule regulates the activity of another molecule. In this talk we will introduce basic concept and basic methods to develop network models using big data.

报告人: 张世华 研究员 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院
题 目: Intelligent spatial transcriptomics: paving the way for deciphering tissue architecture
摘 要: Technological advances in spatial transcriptomics are critical for a better understanding of the structure and function of tissues in biological research. Recently, the combination of intelligent/statistical algorithms and spatial transcriptomics are emerging to pave the way for deciphering tissue architecture. In this talk, I will introduce our efforts to advance intelligent spatial transcriptomics. We first develop a graph attention auto-encoder framework STAGATE to accurately identify spatial domains by learning low-dimensional latent embeddings via integrating spatial information and gene expression profiles. We validate STAGATE on diverse spatial transcriptomics datasets generated by different platforms with different spatial resolutions. STAGATE could substantially improve the identification accuracy of spatial domains, and denoise the data while preserving spatial expression patterns. Importantly, STAGATE could be extended to multiple consecutive sections to reduce batch effects between sections and extract three-dimensional (3D) expression domains from the reconstructed 3D tissue effectively. Based on this, we 1) develop STAMarker for identifying spatial domain-specific variable genes, 2) design STAligner for integrating spatial transcriptomics of multiple slices from diverse biological scenarios, and 3) illustrate the effectiveness of the graph attention auto-encoder for spatial clustering of spatial metabolomics.
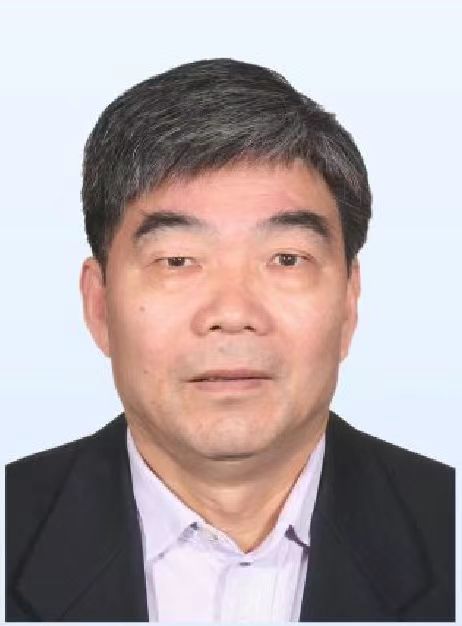

报告人: 徐兴旺 教授 南京大学
题 目: 曲线的一些整体性质
摘 要: 我们将对平面曲线和空间曲线的整体性质进行介绍。对于平面曲线,我们将介绍等周不等式、旋转指标、指标定理及四顶点定理等内容。对于空间曲线,我们将介绍球面上的Crofton公式、空间曲线的全曲率、Fary-Milnor theory及空间曲线的全挠率等内容。
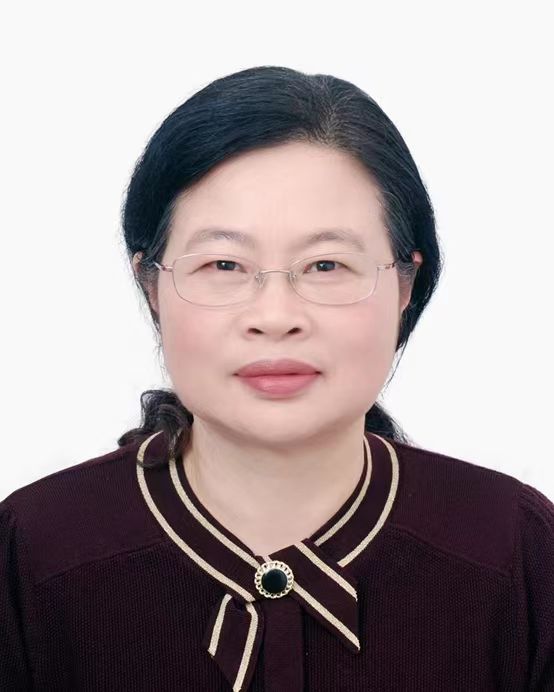

报告人: 邹秀芬 教授 武汉大学
题 目: 生物医学问题的数学理论与方法
摘 要: 在传染病、癌症等复杂疾病的研究中产生了海量的数据,急需发展新的数学理论与方法有效地解析这些数据从而辅助疾病的诊断和治疗。本报告首先介绍数学与生物医学交叉研究领域的国家重大需求和前沿进展,然后通过几个实例来说明数学在交叉学科领域的重要性,包括大规模网络推断的算法,癌症的个性化治疗策略的优化设计等。